Search
Search Funnelback University
11 -
60 of
67
search results for `Research News`
Fully-matching results
-
Resolution ready to shine down under
Duration: 00:01:54
Published Date: 2013/08/29Built by undergraduates working for their exams, with funds raised by the students themselves, Cambridge's solar car is the only British entry into the World Solar Challenge. Despite the odds, however, its radical design could still secure victory. - See more at: http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/resolution-ready-to-shine-down-under#sthash.J5JFhIVd.dpuf -
KSR2 mutations are associated with obesity, insulin resistance and…
Duration: 00:03:06
Published Date: 2013/10/25Researchers from the University of Cambridge have discovered a novel genetic cause of severe obesity which, although relatively rare, demonstrates for the first time that genes can reduce basal metabolic rate -- how the body burns calories. http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/novel-genetic-mutations-cause-low-metabolic-rate-and-obesity -
Meet the robot avatars helping Cambridge students combine education…
Duration: 00:03:41
Published Date: 2018/04/26They are 40cm tall, made of white plastic, and don’t look like your average students, but robot avatars have taken their place in the classroom at Cambridge University – to help two mothers with new-born babies continue their Masters degrees in Genomic Medicine. http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/meet-the-robot-avatars-helping-cambridge-students-combine-education-and-motherhood -
Volvox embryo turning itself inside out
Duration: 00:01:19
Published Date: 2015/04/27Researchers have captured the first 3D video of a living algal embryo turning itself inside out, from a sphere to a mushroom shape and back again. The results could help unravel the mechanical processes at work during a similar process in animals, which has been called the “most important time in your life.” Read more at: http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/upside-down-and-inside-out -
Face of the future rears its head
Duration: 00:04:30
Published Date: 2013/03/19Meet Zoe: a digital talking head which can express human emotions on demand with "unprecedented realism" and could herald a new era of human-computer interaction. The system, called "Zoe", is the result of a collaboration between researchers at Toshiba's Cambridge Research Lab and the University of Cambridge's Department of Engineering. -
Curious Objects: Decorated slippers
Duration: 00:00:41
Published Date: 2016/12/21Why does one of the world's great research libraries have ectoplasm, a spirit trumpet and beard hair posted to Charles Darwin? The answers lie within 'Curious Objects' at Cambridge University Library, which runs until March 2017 and is open free to the public. For more information about Curious Objects, click here: -
Plant ‘thermometer’ triggers springtime budding by measuring…
Duration: 00:01:58
Published Date: 2016/10/28A photoreceptor molecule in plant cells has been found to moonlight as a thermometer after dark – allowing plants to read seasonal temperature changes. Scientists say the discovery could help breed crops that are more resilient to the temperatures expected to result from climate change. Find out more here: -
Not all monkeys are fooled by magic.
Duration: 00:01:25
Published Date: 2023/04/04By performing a famous magic trick, the French Drop, for three species of monkey with differing hand structures, scientists have discovered that – in order to deceive – a conjuror needs the same anatomy as their audience. Read more here- https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/sleight-of-hand-magic-trick-only-fools-monkeys-with-opposable-thumbs -
To boldly go -- how personality predicts social learning in baboons
Duration: 00:01:44
Published Date: 2014/03/11Like other social animals, baboons learn from each other about which foods are best to eat. Now, researchers at Cambridge have found that how well they learn from others depends on their personality, bold or anxious baboons learning more than those who are shy or laid back. - See more at: -
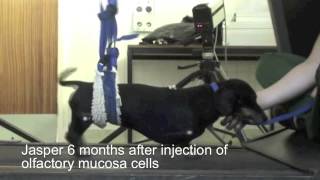
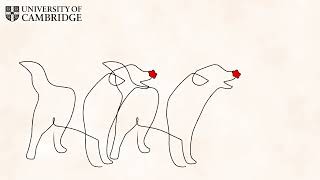
A dog called Jasper during trial to show spinal cord regeneration
Duration: 00:00:46
Published Date: 2012/11/19In a unique collaboration between the University's Veterinary School and MRC's Regenerative Medicine Centre, scientists used a unique type of cell to regenerate the damaged part of the dogs' spines. The researchers are cautiously optimistic that the work could have a future role in the treatment of human patients with similar injuries if used alongside other treatments. For more information, go -
A virtual reality journey through a tumour
Duration: 00:01:33
Published Date: 2017/02/10Scientists at the University of Cambridge are leading an international project to develop 3D versions of breast tumours, which can be studied using virtual reality, thanks to a £20 million award from Cancer Research UK. This will allow scientists and doctors to study every cell and aspect of a tumour in unprecedented detail and could change how the disease is diagnosed, treated and managed. http: -
Uncovering the first European church in the tropics
Duration: 00:15:04
Published Date: 2015/11/06A church has been uncovered on Cabo Verde’s Santiago Island, off the West African coast, which dates back to late 15th century, when Portugal colonised the islands that were later to play a highly strategic role in the global trade in African slaves. Archaeological excavations are helping Cabo Verdeans gain new insight into their remarkable and long-obscured history. Find out more here: -
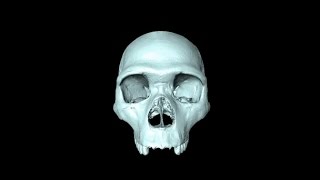
‘Virtual fossil’ reveals last common ancestor of humans and…
Duration: 00:01:47
Published Date: 2015/12/18New digital techniques have allowed researchers to predict structural evolution of the skull in the lineage of Homo sapiens and Neanderthals, in an effort to fill in blanks in the fossil record, and provide the first 3D rendering of their last common ancestor. Here, lead researcher Dr. Aurélien Mounier from Cambridge's Leverhulme Centre for Human Evolutionary Studies describes part of the -
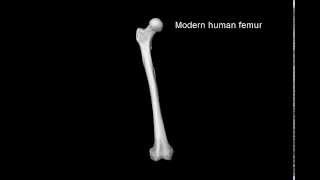
Forager past shows our fragile bones result from physical inactivity…
Duration: 00:01:05
Published Date: 2014/12/23New research across thousands of years of human evolution shows that our skeletons have become much lighter and more fragile since the invention of agriculture - a result of our increasingly sedentary lifestyles as we shifted from foraging to farming. This video shows the CT scanning used in this research. To find out more, visit: -
The Story of Campath -1H
Duration: 00:31:18
Published Date: 2013/09/17A transformational new treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS) - the result of over three decades of research in Cambridge -- has now been approved by the EU agency responsible for regulating new drugs. In recognition of the highly effective new treatment, the University of Cambridge has produced this video which explores the history of the drug, showing the many challenges as well as successes -
Better hygiene in wealthy nations may increase Alzheimer's risk
Duration: 00:03:32
Published Date: 2013/09/04In this video, Gates Cambridge Alumna Dr Molly Fox discusses her research which suggests that people living in industrialised countries may be more likely to develop Alzheimer's. This points to what's known as the 'hygiene hypothesis', the theory that the greatly reduced contact with bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms in the developed world can lead to a weaker immune system and increased -
Electron 'spin' key to solar cell breakthrough
Duration: 00:01:17
Published Date: 2013/08/08In a new paper published in Nature, researchers at the Cavendish Lab used the quantum technique of electron 'spin' to enhance the power of organic solar cells, a much cheaper and more flexible alternative to the current commercial silicon-based solar cells. Find out more here: http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/electron-spin-key-to-solar-cell-breakthrough-0 To do it, they used lasers - and lots -
The best or worst thing to happen to humanity
Duration: 00:05:25
Published Date: 2016/10/19Stephen Hawking helps to launch Centre for the Future of Intelligence Artificial intelligence has the power to eradicate poverty and disease or hasten the end of human civilisation as we know it – according to a speech delivered by Professor Stephen Hawking this evening. For more information and a transcript of Professor Hawking's speech, click here: -
Three-dimensional reconstruction of a rangeomorph
Duration: 00:00:08
Published Date: 2016/11/14New three-dimensional reconstructions show how some of the earliest animals on Earth developed, and provide some answers as to why they went extinct. http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/how-some-of-the-first-animals-lived-and-died A bizarre group of uniquely-shaped organisms known as rangeomorphs may have been some of the earliest animals to appear on Earth, uniquely suited to ocean conditions 575 -
Fossilised dinosaur brains
Duration: 00:02:12
Published Date: 2016/10/27An unassuming brown pebble, found more than a decade ago by a fossil hunter in Sussex, has been confirmed as the first example of fossilised brain tissue from a dinosaur. The fossil, most likely from a species closely related to Iguanodon, displays distinct similarities to the brains of modern-day crocodiles and birds. Learn more here: -
Airflow across a wing
Duration: 00:01:14
Published Date: 2012/01/20"It is often said that the lift on a wing is generated because the flow moving over the top surface has a longer distance to travel and therefore needs to go faster. This common explanation is actually wrong." Here, aerodynamics expert Professor Holger Babinsky from the University of Cambridge's Department of Engineering debunks a popular, yet misleading, explanation of how wings lift. For more -
The Vaccine for Fake News
Duration: 00:07:01
Published Date: 2021/11/25Sander van der Linden has a nickname: Cambridge’s professor of “defence against the dark arts”. His team works with governments and organisations such as Google to find ways to fight against misinformation, disinformation and conspiracy theories. Watch Sander explain his radical idea: that people can be “inoculated” against falling for fake news. Want to be involved in the research? -
Dr Iris Möller - Department of Geography - University of Cambridge
Duration: 00:01:59
Published Date: 2017/03/10Dr Iris Möller of the Cambridge Coastal Research Unit at the Department of Geography of the University of Cambridge explains how an understanding of natural processes and landforms can help us develop win-win solutions for reducing flood risk. Her international collaborative research team has been able to prove that coastal salt marsh protects sea defences during storm. When submerged in up to 2 -
The man we love to hate: it’s time to reappraise Thomas Robert Malthus
Duration: 00:03:56
Published Date: 2016/05/19Thomas Robert Malthus, who was born 250 years ago, became notorious for his ‘principle of population’. He argued that, because poverty was inevitable, some people would not find a seat at ‘nature’s table’ and would perish. In a new book, historians at Cambridge and Harvard set the life and work of this contentious thinker within a wider context – and look in particular at his -
Nataruk: Evidence of a prehistoric massacre
Duration: 00:06:58
Published Date: 2016/01/20Skeletal remains of a group of foragers massacred around 10,000 years ago on the shores of a lagoon is unique evidence of a violent encounter between clashing groups of ancient hunter-gatherers, and suggests the “presence of warfare” in late Stone Age foraging societies. Listen to researchers from Cambridge's Leverhulme Centre for Human Evolutionary Studies discuss the findings, and what they -
Artificial ‘brain’ reveals why we can’t always believe our eyes
Duration: 00:01:20
Published Date: 2021/02/25A computer network closely modelled on part of the human brain is enabling new insights into the way our brains process moving images - and explains some perplexing optical illusions. Find out more here: https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/artificial-brain-reveals-why-we-cant-always-believe-our-eyes This research was supported by the Leverhulme Trust and the Isaac Newton Trust. Reference Rideaux, -
Chimpanzees have favourite ‘tool set’ for hunting staple food of army …
Duration: 00:01:10
Published Date: 2014/10/16New research shows that chimpanzees search for the right tools from a key plant species when preparing to ‘ant dip’ - a crafty technique enabling them to feast on army ants without getting bitten. In the first clip, a female chimpanzee is shown 'ant-dipping' using the ideal tool made from the shrub Alchornea hirtella as a male chimpanzee looks on with envy. The second clip captures a -
How do we reduce the risk of animal viruses jumping to humans?
Duration: 00:04:55
Published Date: 2020/11/09COVID-19 is caused by a virus that jumped from animals to humans - and then spread rapidly. The risk of this happening again, causing another pandemic, is very real. Cambridge researchers have looked at all the major ways this might happen, to work out what might be done to reduce the risk. Read more here: -
The eyes have it
Duration: 00:01:44
Published Date: 2014/02/05Researchers in Cambridge and Exeter have discovered that jackdaws use their eyes to communicate with each other -- the first time this has been shown in non-primates. While what humans do with their eyes has been well studied, we know almost nothing about whether birds communicate with members of the same species with their eyes. The new study, published today in Biology Letters, shows that -
Living with the Inugguit
Duration: 00:10:02
Published Date: 2011/11/24In 2010, Dr Stephen Leonard embarked on a year-long trip to live with the Inugguit of north-west Greenland, the northernmost settled people on Earth. His aim was to record the language, stories and songs of these communities. The traditional life of the community and its future is potentially threatened by a number of factors, one of which is climate change. Dr Leonard lived as a member of those -
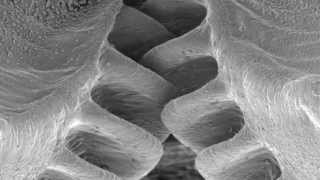
Mechanical gears in jumping insects
Duration: 00:03:42
Published Date: 2013/09/13Previously believed to be only man-made, a natural example of a functioning gear mechanism has been discovered in a common insect - the plant-hopper Issus - showing that evolution developed interlocking cogs long before we did. Professor Malcolm Burrows talks about finding the bugs that led to the science, and working with artists Elizabeth Hobbs and Emily Tracy and members of the community in -
Carmina qui quondam (excerpt) - Boethius, Consolation of Philosophy…
Duration: 00:01:20
Published Date: 2016/04/22April 2016 saw the first performance of reconstructed 11th-Century ‘lost songs’ that hadn’t been heard in over 1,000 years - a performance made possible by the research of one of our lecturers (http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/first-performance-in-1000-years-lost-songs-from-the-middle-ages-are-brought-back-to-life-0) Two years on, a CD of this repertoire has just been released, and we are -
Curious Objects: Tobacco Stopper
Duration: 00:00:40
Published Date: 2016/11/07Billions of words, millions of books, 600 years of Curious Objects. Cambridge University Library is celebrating its 600th anniversary with an exhibition of the weird and wonderful objects in its collections. This rather curious object comes from 18th century England and features a splendid rendering of the man who brought us Hamlet, Macbeth …and invented the word puke! Yes, it’s the Bard -
Meerkats playing
Duration: 00:01:38
Published Date: 2016/11/14Professor Tim Clutton-Brock has been studying the same meerkat groups for over twenty years. He said: "Meerkats are intensely social and all group members engage in bouts of wrestling, chasing and play fighting, though juveniles and adolescents play more than adults. Since they live together in such close proximity and interact many times each day, it is unsurprising that individual meerkats are -
Pythagoras was wrong: there are no universal harmonies!
Duration: 00:01:34
Published Date: 2024/02/28According to Pythagoras, ‘consonance’ – a pleasant-sounding combination of notes – is produced by special relationships between simple numbers such as 3 and 4. More recently, scholars have tried to find psychological explanations, but these ‘integer ratios’ are still credited with making a chord sound beautiful, and deviation from them is thought to make music ‘dissonant’, -
Curious Objects: Luminous Trumpet
Duration: 00:00:40
Published Date: 2016/11/22Why does one of the world's great research libraries have ectoplasm, a spirit trumpet and beard hair posted to Charles Darwin? The answers lie within 'Curious Objects' at Cambridge University Library, which runs until March 2017 and is open free to the public. This Curious Object broadcasts voices from the beyond using the medium of…mediums. Apparently, the ‘Two Worlds’ spirit trumpet would -
Heu quam praecipiti (excerpt) - Boethius, Consolation of Philosophy…
Duration: 00:01:01
Published Date: 2016/04/22April 2016 saw the first performance of reconstructed 11th-Century ‘lost songs’ that hadn’t been heard in over 1,000 years - a performance made possible by the research of one of our lecturers (http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/first-performance-in-1000-years-lost-songs-from-the-middle-ages-are-brought-back-to-life-0) Two years on, a CD of this repertoire has just been released, and we are -
Screaming in space
Duration: 00:00:08
Published Date: 2012/10/26The Cambridge University Spaceflight Society are loading screams onto a smartphone that will be blasted into outer space later this year. The public are invited to submit their screams, which will be emitted while in orbit at the same time as the phone records - to test if it's possible to capture the sound of screaming in space. Members of the University's Office of External Affairs and -
Curious Objects: Ganjifa
Duration: 00:00:40
Published Date: 2017/01/12“These Curious Objects are Ganjifa - playing cards and card games from India, Iran and the Arab world, and are thought to date from the early 18th century. Made of tortoiseshell and finely decorated, they must have belonged to someone absolutely minted. Introduced into India by the Mughals, the game of chance played with these cards was popular from the 16th to the 18th century. Play your cards -
Reconstructing the Songs of Boethius’ Consolation of Philosophy
Duration: 00:13:05
Published Date: 2016/08/17April 2016 saw the first performance of reconstructed 11th-Century ‘lost songs’ that hadn’t been heard in over 1,000 years - a performance made possible by the research of one of our lecturers (http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/first-performance-in-1000-years-lost-songs-from-the-middle-ages-are-brought-back-to-life-0) Two years on, a CD of this repertoire has just been released, and we are -
Calls vs. balls: An evolutionary trade-off
Duration: 00:04:04
Published Date: 2015/10/22Howler monkeys are about the size of a small dog, weighing around seven kilos, yet they are among the loudest terrestrial animals on the planet, and can roar at a similar acoustic frequency to tigers. Evolution has given these otherwise lethargic creatures a complex and powerful vocal system. For males, a critical function of the roar is for mating: to attract females and scare off rival males. -
'Polluted' stellar graveyard gives glimpse of our Solar…
Duration: 00:00:11
Published Date: 2013/05/09By chemically sampling the atmospheres of two dead stars in the Hyades cluster 150 light years away, researchers at Cambridge and NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have discovered the building blocks for Earth-sized planets formed around the stars while they lived. The study offers insight into what will happen in our solar system when our Sun burns out 5 billion years from now. This animation is an -
CTVT Oronasal Tumours
Duration: 00:01:44
Published Date: 2022/07/04Read more about the research here: https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/male-dogs-four-times-more-likely-to-develop-contagious-cancer-on-nose-or-mouth-than-females Animation Credit: Emma Werner Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumour (CTVT) is an unusual cancer – it is infectious and can spread between dogs when they come into contact. The living cancer cells physically ‘transplant’ themselves -
Scientists to tackle mysteries of teenage brain
Duration: 00:00:20
Published Date: 2013/05/15Despite adolescence being a high-risk time for developing major psychiatric and drug dependence disorders, very little is known about the teenage brain. A novel research project jointly led by scientists from the University of Cambridge and UCL (University College London) aims to shed light on what happens to the brain as young people mature as part of a £5.4 million project funded by the -
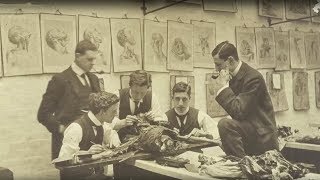
The Body Snatchers: Corpse and Effect
Duration: 00:04:25
Published Date: 2012/10/30When you bury family members in a cemetery, you expect them to stay there. Not so 200 years ago, however, when body snatchers prowled the nation's burial grounds looking for subjects. An acute shortage of bodies eligible for dissection by student doctors in the late 17th century drove this cottage industry until the Anatomy Act of 1832, when dead bodies of all the unclaimed poor could legally -
Anglo-Saxon teen buried in bed with gold cross
Duration: 00:05:12
Published Date: 2012/03/16One of the earliest Anglo-Saxon Christian burial sites in Britain has been discovered in a village outside Cambridge. The grave of a teenage girl from the mid 7th century AD has an extraordinary combination of two extremely rare finds: a 'bed burial' and an early Christian artefact in the form of a stunning gold and garnet cross. The girl, aged around 16, was buried on an ornamental bed -- a very -
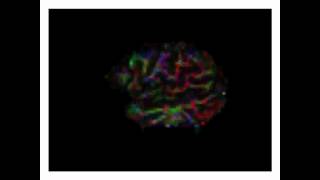
Brain cells from skin cells
Duration: 00:01:02
Published Date: 2012/02/24This is a beautiful image of human brain cells, which can now be grown from adult skin cells. Cambridge University's Under the Microscope is a collection of videos that show glimpses of the natural and man-made world in stunning close-up. Check out the rest of the series here: http://bit.ly/A6bwCE Yichen Shi: "Brain neural stem cells derived from human skin cells: these stem cells express typical -
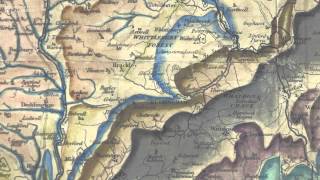
The Magna Carta of scientific maps
Duration: 00:04:02
Published Date: 2015/08/03One of the most important maps of the UK ever made – described as the ‘Magna Carta of geology’ – is to go on permanent public display in Cambridge after being restored to its former glory. - See more at: http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/the-magna-carta-of-scientific-maps#sthash.cfVPSGJz.dpuf William Smith’s 1815 Geological Map of England and Wales, which measures 8.5ft x 6ft, -
AI that predicts progress of Alzheimer's disease
Duration: 00:03:15
Published Date: 2024/07/13Learn more here: https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/artificial-intelligence-outperforms-clinical-tests-at-predicting-progress-of-alzheimers-disease Scientists have developed an artificially-intelligent tool capable of predicting in four cases out of five whether people with early signs of dementia will remain stable or develop Alzheimer’s disease. This new approach could reduce the need for -
Minecraft tree “probably” the tallest tree in the Tropics
Duration: 00:02:52
Published Date: 2016/06/07A tree the height of 20 London double-decker buses has been discovered in Malaysia by conservation scientists from the University of Cambridge monitoring the impact of human activity on the biodiversity of a pristine rainforest. The Yellow Meranti stands 89.5m tall in an area of forest known as ‘Sabah’s Lost World’ – the Maliau Basin Conservation Area, one of Malaysia’s last few
Refine your results
Date
- 67 Uncertain
Search history
Recently clicked results
Recently clicked results
Your click history is empty.
Recent searches
Recent searches
Your search history is empty.